This is "Titration of an Organic Acid", from the book 32 Weeks of OChem (v. 1.0).
Titration of an Organic Acid
Learning Objectives
- To perform the steps required to prepare a standardized solution of sodium hydroxide.
- To properly record data and calculations in a lab notebook.
- To measure the neutralization equivalent of an unknown carboxylic acid.
- To perform the steps required in a titration.
- To create a titration curve.
- To determine the identity of an unknown acid.
- To recognize a carboxyl group.
- To distinguish between the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base..
- To know how to use a pKa table to predict the direction of an acid base reaction.
- To be able to write a reaction mechanism including a proton transfer step.
Recall from general chemistry that we can titrate acids with a strong base and make phenolphthalein turn that really cool color.
Figure 1.1 (Lab) Acid-Base Titration
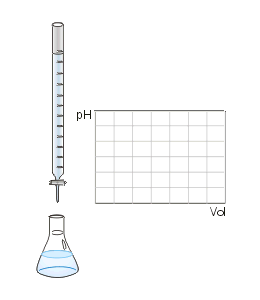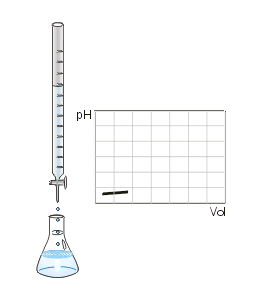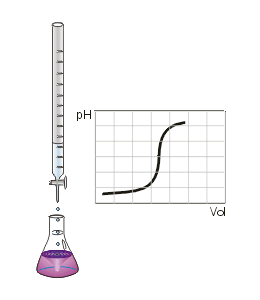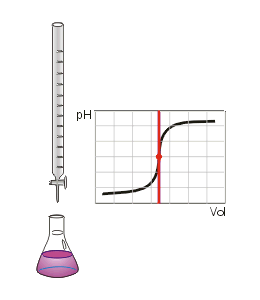
By Luigi Chiesa (Draw by Luigi Chiesa) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
You should read section 1.3 in the textbook.
Part 1
In part 1 of this activity, you will standardize a solution of sodium hydroxide. It is practically impossible to mix up a solution of sodium hydroxide that has a precisely known concentation. Sodium hydroxide is plagued by being hygroscopic (grabbing water from the air) and reacting with the carbon dioxide in the air. To perform a truly meaningful titration with a sodium hydroxide solution, one first has to standardize the sodium hydroxide solution. To do this standardization, you will perform a titration with potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP).
Figure 1.2 (Lab) Potassium hydrogen phthalate
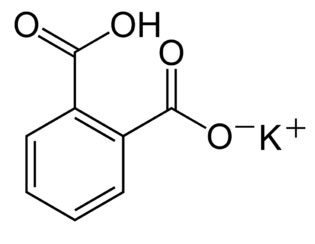
By Bnejah-bmm27, via Wikimedia Commons
Try to use the pKa table in section 1.3 to estimate the pKa of KHP.
KHP is useful as a standard for your titrations because it is a shelf-stable monoprotic acid that is easy to measure precisely.
- Quantitatively prepare 50 mL of an approximately 0.1 M KHP.
- Use the analytical balance to weigh the appropriate amount of solid KHP in a small beaker.
- Dissolve the KHP in an amount of water less than 50 mL.
- Transfer the KHP soln and rinsings to a volumetric flask. Bring to the line with water.
- MIX MIX MIX.
- Titrate a solution of approximately 0.1 M NaOH to the endpoint.
- Use a pipet to measure 10.00 mL of the KHP solution into a 125-mL erlenmeyer.
- Rinse and fill a buret with the NaOH soln. Remember to get rid of the air bubble.
- Add 1 drop of phenolphthalein indicator.
- Add the NaOH soln until a pink hue persists in the solution for 5 seconds.
Scoring for Part 1
Lab notebook, recorded in ink, for part 1 (4 points):
- Mass of KHP as measured with the analytical balance.
- Initial buret reading to the 0.01 mL
- Final buret reading to the 0.01 mL.
- Calculation of the NaOH soln concentration to the correct significant figures.
Part 2
Dicarboxylic acids have two carboxyl groups (-COOH). You will be assigned an unknown acid from the table below:
Table 1.1 (Lab) Linear Saturated Dicarboxylic Acids
Source: Wikipedia
General formula HO2C(CH2)nCO2H.[1] The PubChem links gives access to a wealth of information on the compounds.
-
n Common name Systematic IUPAC name Structure pKa1 pKa2 PubChem 0 Oxalic acid ethanedioic acid 
1.27 4.27 971 1 Malonic acid propanedioic acid 
2.85 5.05 867 2 Succinic acid butanedioic acid 
4.21 5.41 1110 3 Glutaric acid pentanedioic acid 
4.34 5.41 743 4 Adipic acid hexanedioic acid 
4.41 5.41 196 5 Pimelic acid heptanedioic acid 
4.50 5.43 385 6 Suberic acid octanedioic acid 
4.526 5.498 10457 7 Azelaic acid nonanedioic acid 
4.550 5.498 2266 8 Sebacic acid decanedioic acid 
5192 9 undecanedioic acid 15816 10 dodecanedioic acid 
12736 11 Brassylic acid tridecanedioic acid 10458 12 Thapsic acid hexadecanedioic acid 10459
There is a handy mnemonic device for remembering the first 5 common names, "Oh My! Such Good Apple Pie"
One of the chemical tests one can perform on an unknown is to determine what is called the neutralization equivalent. Simultaneously, we can also create a titration curve for our unknown acid by simply including a pH meter.
- Accurately weigh aproximately 0.2 g of acid into a 250-mL beaker.
- Add about 50 mL of water (amount is not important). Add a stirbar and get the mixture stirring.
- If the acid doesn't all dissolve, it is not important since the reaction with NaOH will make a more water-soluble salt.
- Rinse a pH electrode connected to a freshly calibrated pH meter. Clamp the electrode away from the stirbar.
- Titrate with your standardized NaOH and phenolphthalein indicator to the endpoint and take a buret reading.
- Take lots of buret and pH readings when the pH is changing, not so many when the pH is relatively unchanged.
- Continue adding standardized NaOH and take at least 5 pH readings, at least 5 mL past the endpoint.
Scoring for Part 2
Lab notebook for part 2 includes (6 points):
- Mass of acid.
- Sufficient Buret/pH meter readings
- Endpoint
- Calculation of neutralization equivalent:
Results: Printed and submitted before the beginning of lab next week (20 points).
- Titration Curve
- Structural formula of unknown acid.
- Comparison of your experimental N.E. with









